The establishment of the Bank of England in 1694 marked a turning point in the history of banking. This historic event ushered in the era of modern central banks, which play a fundamental role in national and international economies. In this blog post, we explore the genesis of the Bank of England, its evolution and its impact on modern banking.
The Establishment of the Bank of England
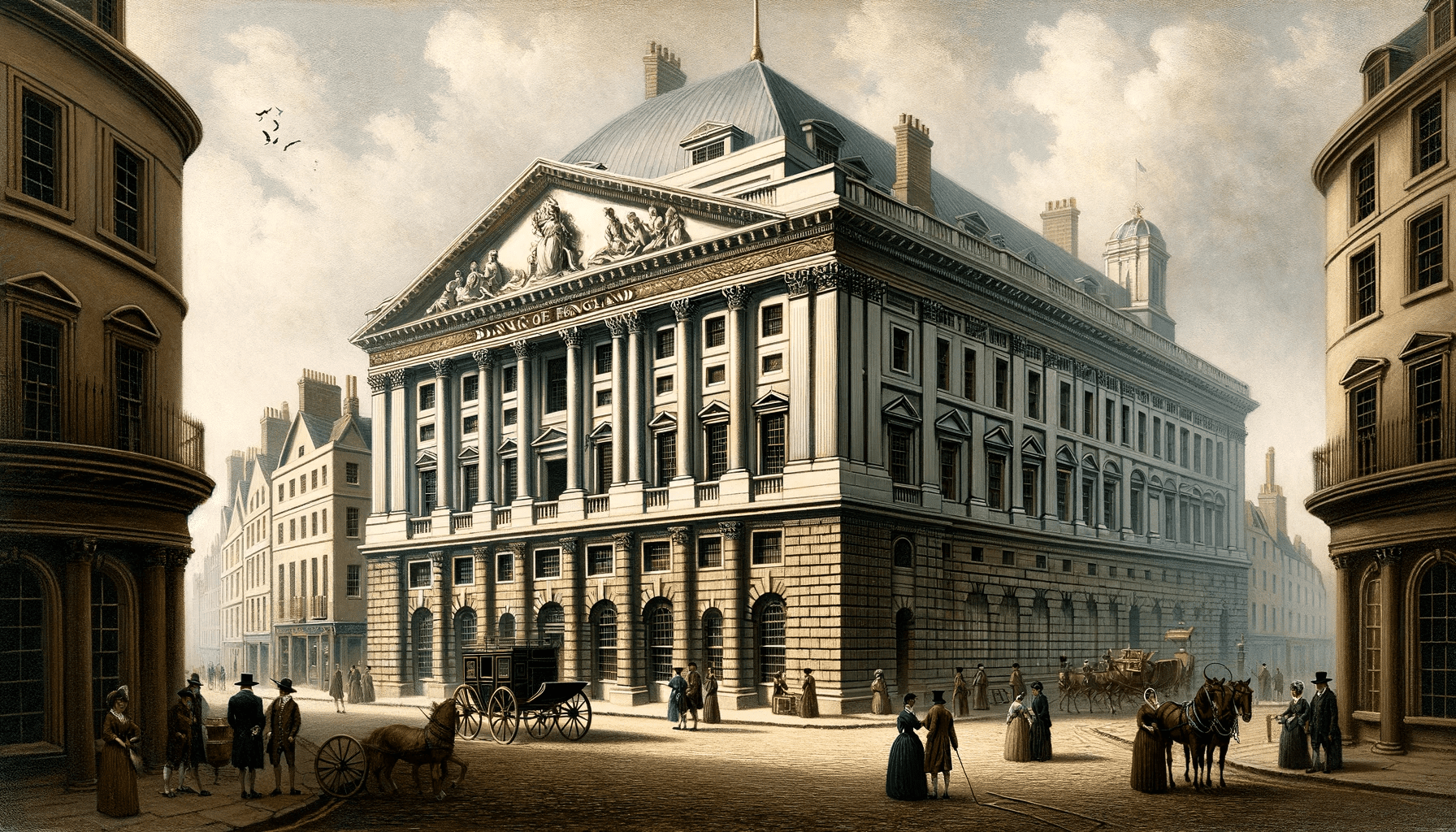
Was founded in 1694, amid political and economic turmoil in England. The country needed resources to finance the war against France, and the creation of a central bank was a revolutionary step to stabilize public finances. The bank began as a private institution that acted as the government’s lender of last resort, but grew into the central pillar of the British financial system.
The First Years of the Bank of England
In its early years, the Bank of England focused mainly on managing public debt and issuing banknotes. This was a new concept: money backed by the bank’s promise, rather than gold or silver. This innovation was a precursor to modern paper money.
Evolution toward a Modern Central Bank
Over the years, the Bank of England expanded its functions. It became responsible for monitoring financial stability, regulating other banks, and implementing monetary policy. This transformation reflected the growing complexity of the economy and the need for a more active central bank role in economic policy.
Innovation and Modernization
The Bank of England was at the forefront of financial innovation. She played a crucial role in the development of modern banking practices, such as the establishment of the minimum reserve and the use of interest rates as a tool for economic steering. These tools are now standard practices for central banks worldwide.
Impact on Modern Banking
The history and evolution of the Bank of England served as a model for other countries in establishing their own central banks. The principles and practices it developed form the basis of modern central banking and are essential to the functioning of contemporary economies.
Contribution to National and International Economies
As a central bank, the Bank of England plays a key role in the British economy, but its influence also extends to international financial markets. It contributes to global financial stability and works with other central banks to address economic challenges.
Bank of England’s conclusion
The Bank of England has not only been a witness to the evolution of banking, but has actively contributed to its formation. From its humble beginnings to its current status as one of the world’s most influential financial institutions, the Bank of England offers a fascinating insight into the modernization of banking and the central role of central banks in our economies.

Leave a Reply